What is Cerebral Infarction?
What is Cerebral Infarction? This condition affects the brain and is a leading cause of death and disability globally. However, there is no international consensus on what constitutes a cerebral infarction. There are three common symptoms of this disease. The first symptom is a sudden onset of yawning, and the second symptom is extreme fatigue. Patients may also experience a lack of strength.
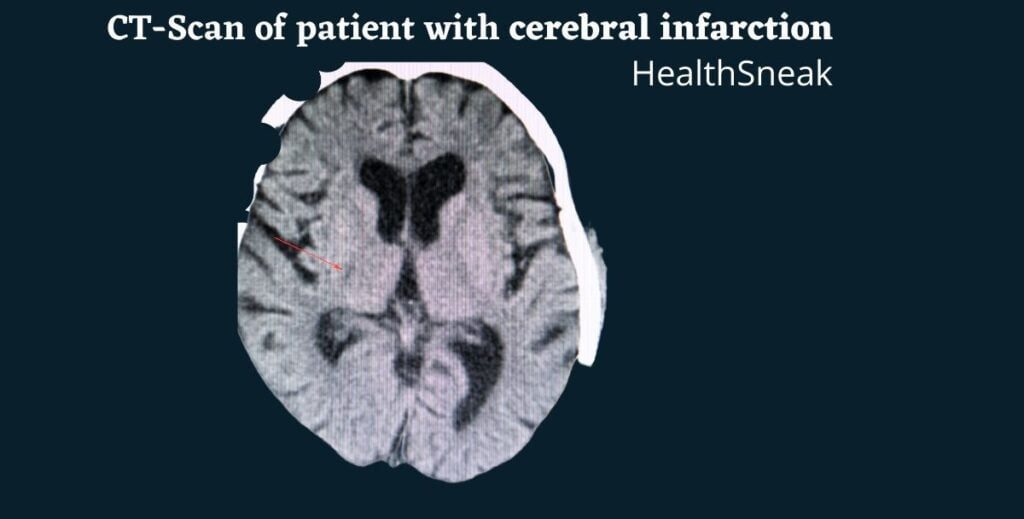
A stroke may be a result of a variety of causes. For example, a tumor in the breast might be a sign of brain cancer, or avascular mass could result from a blood clot. An avascular condition called atherosclerotic plaque or a patent foramen ovale can cause cerebral infarction. The diagnosis is usually made using a CT or MRI scan and an angiography test.
Depending on the type and severity of the cerebral infarction, treatment will vary. The most common treatment is thrombolytic drugs, which are given to patients within 90 minutes of arrival at the hospital. Mechanical embolectomy devices are used to restore blood flow to the ischemic area. When the treatment has not worked, cerebral infarction is often diagnosed after a few days. This disease is treated quickly to reduce the chances of a fatal outcome.
Brief
The symptoms of cerebral infarction vary. For instance, if you’ve had a blood clot in the brain, you may experience a swollen gray or white part of the brain, and a white MRI may show a petechial hemorrhage. Moreover, if you have had a traumatic event such as an accident or a violent assault, a stroke can result in a stroke.
While several underlying causes of cerebral infarction should be diagnosed only when a person experiences a complete or partial loss of brain cells, there are no specific clinical symptoms. It is a symptom of another illness or condition, and a symptom of a stroke is a clear indication that a patient has suffered a cerebral infarction. Likewise, asymptomatic infarction is a silent infarction.
The symptomatic and silent ischemic events of cerebral infarction can be classified as symptomatic and silent. Asymptomatic infarction produces a clinical symptom, and a silent infarction is a central nervous system infarction with no asymptomatic symptoms. But there are many types of this disease, and there are two main types: asymptomatic.
Asymptomatic cerebral infarction
Asymptomatic cerebral infarction is asymptomatic caused by a lack of oxygen and nutrients to the brain. When the blood supply to the brain is interrupted, asymptomatic infarction can be a life-threatening condition. In many cases, the symptoms of cerebral infarction are temporary and treatable. Whether you’re experiencing a stroke symptom or have suffered a cerebral infarction, it can be dangerous and can result in serious consequences.
Definition of Cerebral Infarction
Cerebral infarction is defined as the pathological process that causes the formation of necrotic tissue within the cerebral cortex (cerebral infarct). It results from a deteriorated blood flow (ischemia) and reduced oxygen delivery (hypoxia) typically due to thromboembolism. Cerebral infarction is characterized clinically as a stroke. In response to ischemia, the brain degrades through the process of liquid necrosis
Cerebral Infarction Vs CVA
Cerebral Infarction Vs Cerebrovascular Accident- If you are a doctor, you are likely to hear about the difference between cerebral infarction and cerebrovascular accident (CVA). A blockage causes both conditions in the blood flow to the brain, and either one may result in permanent damage. A stroke is caused by a ruptured artery, while a cerebral infarction is a smaller type of stroke. There is also a difference between a transient ischemic attack and a cerebrovascular accident.
A stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA), interrupts blood flow to the brain. It is the most common cause of disability and death among adults and affects over one million people per year. A stroke is categorized into hemorrhagic and ischemic strokes. Both types result from a blockage or narrowing of an artery. In both cases, the resulting damage is to the brain.
The TIA is associated with a small percentage of death due to stroke and can be classified as a Type III or IV. Symptoms of the cerebrovascular disease include numbness, weakness, nausea, dizziness, and a loss of balance. A TIA can also result in speech and memory problems. Other signs of a stroke include Amaurosis fugax, a visual syndrome characterized by monocular blindness. A doctor can diagnose a TIA based on the presence of these symptoms. A carotid ultrasound and a brain scan are the two most common tests used to determine the difference between CVA and cerebral infarction. However, a positive test never excludes the possibility of a stroke.
Cerebrovascular disease ICD 10
A cerebrovascular infarction is a brain disease generally classified by hemisphere, lobe, arterial distribution, and etiology. It will help if you use these codes for all reimbursement claims with dates of service after October 1, 2015.
The ICD-10-CM coding system provides physicians with the most complete and accurate diagnosis for every patient. Regardless of the infarction type, it is important to use the right code for the right condition.
Symptoms of Cerebral Infarction
The symptoms of cerebral infarction depend on the part of the brain that has been affected. Primary motor cortex infarctions are characterized by weakness and loss of sensation on the opposite side of the body. If the infarction has occurred in the brainstem, it can lead to a syndrome that affects the entire brainstem.
Other common symptoms include:
- Lack of eye movement
- Abnormal pupil dilation
- If it has occurred in the left side of the brain, speech infarction can result in slurred speech.
- Reflexes may also be aggravated in the left side of the brain.
Post-Acute Effects of Cerebral Infarction
Post-acute effects of cerebral infarction can be difficult to understand. In general, they occur months to years after the acute phase of the condition. The following article discusses a few of these consequences and how to identify them. Aftercare may be necessary, but it is always recommended to contact your health care provider after suffering a CVA.
Risk factor of Cerebral Infarction
There are several risk factors of cerebral infarction. These risk factors are mainly modifiable. To reduce the incidence of cerebral infarction, patients should take measures to reduce or eliminate these risks. Prevention is the primary concern of the community. In addition to educating patients about the risk factors, there are also several ways to prevent this condition. These steps include: reducing the occurrence of blood clots in the brain.
Age
Age is one of the main risk factors for cerebral infarction. The risk of a cerebral infarction increases with age. However, the average age of a stroke in Pakistan was 51.5 years. It is unclear whether this difference is attributed to a lack of awareness of risk factors and insufficient control. In addition, the incidence of ischemic stroke is higher in older people, which means that the onset of this condition is more prevalent in older individuals.
The study studied 100 consecutive cases of first-time cerebral infarction in New York City. Most patients had multiple risk factors, including:
- Smoking
- Hypertension
- Ischemic heart disease
- Hyperlipidemia
- Atrial fibrillation
- Obesity
- A family history of stroke.
- Another significant risk factor was physical inactivity, which affected 39% of patients.
Treatment of Cerebral Infarction
Treatment of Cerebral Infarction is critical for preventing or reversing the damage to the brain. It can become fatal if not detected early. The most effective way to diagnose an infarction is to conduct a CT scan of the head and neck. A physician may also use angiography or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in some cases. This test is essential to diagnose an infarction and determine the appropriate treatment. You can read the detailed article on treatment of rheumatoid arthritis.
Medication to treat Cerebral Infarction
Thrombolytic therapy is a treatment of cerebral infarction that involves the injection of a drug into the patient’s vein. The patient will usually receive thrombolytics in the first few hours of stroke, which dissolves the clots in the brain. However, the effect of treatment diminishes with time. Therefore it is best to start the therapy as soon as possible after the stroke.
Removing the clot
One of the most effective treatments for cerebral infarction involves removing the clot. A catheter is inserted into the femoral artery and directed to the cerebral circulation. A corkscrew-like device is then used to catch the chunk and remove it. The procedure is usually successful within six to twenty-four hours. Surgical intervention may be necessary if a clot is found.
Stenting and Angioplasty
Stent retrieval is another type of thrombectomy. The clot is removed using a wire-cage device called a stent retriever. Special suction tubes may be used to remove the clot. The endovascular procedure is important for patients with a stroke within 6 hours. Fortunately, newer imaging technology has extended the time window of stent retrievals.
Surgery
Surgery to open the carotid artery is also an option for acute ischemic stroke. A surgeon will make a small incision in the neck and remove the plaque to prevent a thrombus from forming. After the surgery, the patient may experience numbness or tingling in the face or tongue. Thankfully, this temporary nerve damage is usually not serious and requires treatment.
Patients with Diabetes
Patients suffering from an ischemic stroke should be evaluated for high blood pressure and diabetes, common risk factors for cerebral infarction. Diagnosis and treatment of this disorder will include identifying the underlying cause and preventing future complications. Surgery for decompression and evacuation is typically the only option for patients suffering from a massive cerebellar infarction. The brain is opened up during surgery, and the infarction is removed, and the patient can then recover.
Please let us know in the comment section if some other treatment works for you.